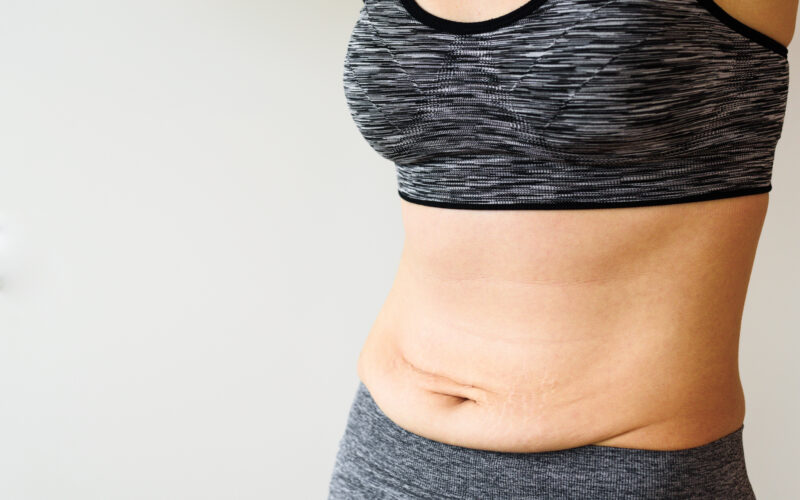
My wife tells the story of a colleague who once asked if my extremely fit wife thought that she, her colleague, was fit. Dana responded, “No, you do not exercise, so you can’t be fit.” The woman responded, “But I am not fat.” Dana responded, ” I didn’t say you were fat, just not fit,” and the skinny fat dilemma began.
Table of Contents
Skinny fat is a term used to describe a body type that appears thin but has a high percentage of body fat. This body type is characterized by a lack of muscle mass and a higher proportion of body fat, which can lead to health problems. People who are skinny fat may have a higher risk of developing conditions such as diabetes, heart disease, and metabolic syndrome.
It’s important to note that “skinny fat” is not a medical diagnosis but a colloquialism used to describe a specific body type. Skinny fat individuals may appear healthy outside, but their internal health may be compromised due to their high body fat levels.
Maintaining a healthy diet and regular exercise can help prevent or reverse the effects of being skinny and fat. It’s crucial for individuals who fall under this category to focus on building muscle mass while reducing their overall body fat percentage.
One way to achieve this is through resistance training, which involves lifting weights or using resistance bands to build muscle strength and size. Cardiovascular exercises like running or cycling can also help burn excess calories and reduce overall body fat.
Another critical aspect of combating skinny fat is maintaining proper nutrition. Eating foods rich in protein, healthy fats, and complex carbohydrates can support muscle growth while reducing overall calorie intake.
Avoiding processed foods and sugary drinks can help reduce inflammation and improve overall health markers such as blood sugar levels and cholesterol.
Understanding the Skinny Fat Body Type
The Risks of Being Skinny Fat
Subcutaneous fat, the type of fat that accumulates just beneath the skin, is often overlooked and underestimated. People who appear slim but have a high percentage of subcutaneous fat are known as skinny fat. This body type can be deceptive because it does not necessarily indicate good health. Skinny fat individuals may be at greater risk for developing metabolic disorders such as diabetes and heart disease.

Skinny fat individuals are at risk because subcutaneous fat can accumulate around vital organs such as the liver and pancreas, leading to insulin resistance and other metabolic abnormalities. Excess subcutaneous fat can lead to inflammation in the body, which is linked to various health problems, including cancer.
Another factor that contributes to the risks associated with being skinny fat is muscle loss. Many people who appear slim may have low muscle mass due to a sedentary lifestyle or poor nutrition habits. Muscle tissue plays an essential role in regulating metabolism and maintaining overall health. When muscle mass decreases, metabolism slows down, and the body becomes less efficient at burning calories.
Preventing Skinny Fat
Fortunately, some steps can be taken to prevent becoming skinny fat or reduce its risks if you fall into this category. One way is through exercise that includes cardiovascular activity and strength training exercises. Cardiovascular exercise helps burn calories, while strength training builds muscle mass, which increases metabolism.
In addition to exercise, proper nutrition also plays a key role in preventing or reducing the risks associated with being skinny fat. A diet rich in whole foods such as fruits, vegetables, lean proteins, and healthy fats can help regulate metabolism while providing essential nutrients for overall health.

Health Risks of Being Skinny Fat or Metabolically Obese Normal Weight (MONW)
Increased health risks are associated with skinny fat or metabolically obese at normal weight (MONW). MONW is a condition where an individual has a healthy weight but low muscle mass and excess fat. This condition can lead to various health problems, such as type 2 diabetes, heart disease, and metabolic syndrome.
Visceral fat is one of the risk factors for MONW individuals. Visceral fat around the organs can increase insulin resistance, leading to high blood sugar levels. High blood sugar levels can cause damage to various organs in the body, including the kidneys, eyes, and nerves. MONW individuals also have a higher risk of developing cardiovascular diseases due to increased levels of triglycerides and low-density lipoprotein (LDL) cholesterol.
Weight loss and increasing muscle mass through exercise can help reduce the risks associated with MONW. Losing weight helps decrease visceral fat accumulation in the body, which reduces the risk of developing type 2 diabetes and other related diseases. Resistance training exercises such as lifting weights or using resistance bands can help increase muscle mass while reducing body fat percentage.
Disordered eating behaviors can also contribute to the development of MONW. Restrictive diets that limit calorie intake may decrease muscle mass while retaining excess body fat. Eating nutrient-dense foods such as fruits, vegetables, lean proteins, and whole grains can help promote overall health while maintaining a healthy weight.
Identifying a Skinny Fat Body Type
Body composition analysis is the most effective way to identify a skinny fat condition. Despite appearing thin, this condition is characterized by having a high percentage of body fat and low lean muscle mass. It’s important to understand that having a skinny fat body type can be just as dangerous as being overweight or obese.

Lean Body Mass vs. Lean Muscle Mass
Before identifying a skinny fat body type, it’s essential to differentiate between lean body mass and lean muscle mass. Lean body mass refers to the weight of lean tissue, including bones, organs, and muscles. On the other hand, lean muscle mass refers explicitly to the importance of muscle tissue in the body.
While both are crucial components of overall health and fitness, it’s essential to have an appropriate balance between them. Too little lean muscle mass can lead to weakness and poor physical performance, while too much body fat can increase your risk for various health complications.
Body Composition Analysis
A comprehensive body composition analysis test is the most accurate way to determine whether you have a skinny fat condition. These tests measure your total weight, lean body mass, and body fat percentage using specialized equipment such as bioelectrical impedance analysis (BIA), dual-energy X-ray absorptiometry (DEXA), or hydrostatic weighing.

By analyzing these measurements together with other factors such as age, gender, height, and activity level, healthcare professionals can accurately diagnose whether someone has a skinny fat condition or not.
Health Risks Associated with Skinny Fat Condition
A high percentage of body fat coupled with low lean muscle mass increases your risk for several health complications, such as insulin resistance, cardiovascular disease, and metabolic disorders like type 2 diabetes.
Insulin resistance occurs when cells in your muscles don’t respond correctly to insulin hormone produced by the pancreas leading to high blood sugar levels, which may result in type 2 diabetes. Cardiovascular disease includes heart attack, stroke, and high blood pressure. Metabolic disorders like diabetes type 2 occur when your body’s metabolism is disrupted, leading to an inability to regulate blood sugar levels.
How to Tell If You’re Skinny Fat
Low Body Weight but High Body Fat Percentage
You may think being skinny means being healthy, but that’s not always true. This reminds me of a story from my wife that I referenced in the introduction. If you have a low body weight but a high body fat percentage, it could mean you’re “skinny fat.” This term refers to people who look thin on the outside but have a high percentage of body fat.
You can use a body composition test to determine if you’re skinny fat. This test measures your body fat percentage and muscle mass. A healthy range for women is between 18-28%, while men should aim for 10-20%. If your body fat percentage falls outside this range, it’s time to act.
Lack of Muscle Tone and Definition
One of the most significant signs that you’re skinny fat is a lack of muscle tone and definition. Even though your weight may be in a healthy range, your muscles are weak and underdeveloped. This lack of muscle mass can lead to poor posture, back pain, and injury.

Start incorporating strength training exercises into your workout routine to combat this issue. Focus on compound movements like squats, deadlifts, and bench presses to build strength. You can also add in isolation exercises like bicep curls or tricep extensions to target specific areas.
Protruding Belly or Love Handles
Another sign that you’re skinny fat is a protruding belly or love handles. Even though the rest of your body may appear slim, excess belly fat can harm your health. It increases your risk of heart disease, diabetes, and other chronic illnesses.
To reduce belly fat and love handles, focus on eating a balanced diet with plenty of protein and fiber. Avoid processed foods high in sugar and unhealthy fats as much as possible. Incorporate cardio exercises like running or cycling to burn calories and boost metabolism.
Thin Arms and Legs Without Muscle Mass
If you have thin arms and legs without muscle mass, it’s another sign that you’re skinny fat. Even though your limbs may appear slim, they lack the strength and definition of healthy muscles. This can lead to poor balance, coordination, and mobility.
To build muscle in your arms and legs, focus on exercises like push-ups, pull-ups, lunges, and squats. These movements target multiple muscle groups at once and promote overall strength. You can also add in resistance bands or weights to increase the intensity of your workouts.
Weakness and Lack of Stamina During Physical Activities
Feeling weak and lacking stamina during physical activities could be a sign that you’re skinny fat. Without proper muscle mass and cardiovascular health, your body struggles to meet physical demands. This can lead to fatigue, shortness of breath, and even injury.
Incorporate cardio exercises like running or cycling to improve your endurance and stamina. Start slow and gradually increase the intensity over time. You can also try high-intensity interval training (HIIT) to boost metabolism and burn calories.
High Processed Food Diet Low in Protein
Finally, if your diet is high in processed foods but low in protein, it could contribute to being skinny fat. Processed foods are often high in sugar and unhealthy fats that can lead to weight gain. A lack of protein can also hinder muscle growth and repair.

To combat this issue, focus on eating whole foods like fruits, vegetables, lean meats, and nuts/seeds as much as possible. Aim for a balanced diet with plenty of protein from sources like chicken breast or fish fillet for optimal health benefits.
Improving Health and Gauging Body Fat Percentage
Importance of Measuring Body Fat Percentage
Maintaining a healthy body composition is crucial for overall health and well-being. Increased body fat can lead to various health problems, including heart disease, diabetes, and high blood pressure. Therefore, measuring body fat percentage is essential in determining one’s overall health and assessing the risk of developing these health problems.
Body Composition Scales and Calipers
Body composition scales and calipers are effective tools in measuring body fat percentage and providing accurate body composition results. Body composition scales use bioelectrical impedance analysis (BIA) to measure the resistance of electrical flow through the body. This measurement helps determine the amount of lean muscle mass versus fat mass in the body. On the other hand, calipers use skinfold measurements to estimate subcutaneous fat storage.

It is important to note that while both methods provide accurate results, they also have limitations. For example, BIA may not be as accurate for individuals with high hydration levels or those with pacemakers or defibrillators. Calipers may also be less accurate for individuals with loose skin or excessive subcutaneous fat.
Focus on Maintaining Healthy Body Composition
It is important to focus on maintaining a healthy body composition rather than just reducing body weight. Muscle mass plays a significant role in overall health, as it helps improve metabolism and maintain bone density. Fat ranges vary based on age and gender.
For example, a healthy range for women aged 20-39 is between 21-32% body fat, while men within the same age group should aim for 8-19%. As we age, our bodies tend to store more fat, meaning that older adults will require higher ranges than younger adults.
Adding Healthy Habits and Causes of Skinny Fat
Poor Lifestyle Habits and Causes of Skinny Fat
Lifestyle habits play a significant role in the development of skinny fat. People who lead sedentary lifestyles and consume unhealthy foods are likelier to develop skinny fat. Skinny fat is a condition where a person appears thin but has a high body fat percentage, which can lead to health problems such as diabetes, cardiovascular disease, and metabolic syndrome.
Lack of Exercise
One of the primary causes of skinny fat is lack of exercise. When people do not engage in physical activity, they lose muscle mass and gain body fat. This leads to an increase in body fat percentage, even if their weight remains the same. Moreover, when muscles are not used regularly, they become weak and flabby. Therefore, incorporating strength training exercises into one’s routine can help build muscle mass and prevent skinny fat.
Unhealthy Eating
Another cause of skinny fat is unhealthy eating habits. Consuming too much processed food and sugar can lead to insulin resistance, a common cause of skinny fat. Insulin resistance occurs when cells become resistant to insulin’s effects on glucose uptake from the bloodstream into cells for energy production. As a result, glucose accumulates in the bloodstream, increasing blood sugar levels that promote weight gain.
Hormonal Imbalances
Hormonal imbalances can also contribute to the development of skinny fat. Women with polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS) have higher levels of male hormones called androgens than normal levels leading them prone to gain weight around their midsection area, causing them to appear thin but with a high body fat percentage.
Aging
As we age, our metabolism slows down, making it easier to gain weight while losing muscle mass simultaneously, increasing body fat percentage.
Stress & Lack Of Sleep
Lastly, stress and lack of sleep can also contribute significantly towards developing skinny fats as cortisol hormone levels increase due to stress, increasing body fat percentage.
Incorporating Healthy Habits
One must incorporate healthy habits into one’s lifestyle to prevent and reduce skinny fat. Strength training exercises such as weightlifting, resistance band training, or calisthenics can help build muscle mass and improve metabolic rate. Eating a balanced diet with lean protein, complex carbohydrates, and healthy fats can help prevent skinny fat. Moreover, getting enough sleep and managing stress can help maintain a healthy weight.
Workouts to Help Combat Skinny Fatness: Concurrent Training
Strength Training: Building Muscle to Combat Skinny Fatness
Strength and weight training effectively build muscle and increase skeletal muscle mass, which can help combat skinny fatness. When you engage in strength training, your muscles undergo stress that causes them to break down. As they repair themselves, they grow stronger and larger, leading to an increase in muscle mass. This process is called hypertrophy.

To build muscle effectively, it’s important to focus on compound movements that target multiple muscle groups at once. Examples of compound exercises include squats, deadlifts, bench press, pull-ups, and rows. These exercises allow you to lift heavier weights and engage more muscles at once than isolation exercises like bicep curls or leg extensions.
It’s also important to progressively overload your muscles by gradually increasing the weight you lift over time. This will ensure that your muscles continue to adapt and grow stronger.
Cardio: Losing Fat While Maintaining or Building More Muscle
Incorporating cardio into your workout routine can aid in losing fat while maintaining or building more muscle. Cardiovascular exercise increases your heart rate and burns calories, which can help create a calorie deficit necessary for weight loss.

However, it’s important not to rely solely on cardio for weight loss as this can lead to losing fat and muscle mass. Instead, focus on high-intensity interval training (HIIT), which involves short bursts of intense exercise followed by rest or low-intensity activity periods.
HIIT is more effective at burning fat while preserving lean body mass than steady-state cardio, like jogging or cycling for long periods.
Preventing Muscle Loss: Focus on Strength Training
When trying to lose fat through dieting or cardio alone, there is a risk of losing muscle and fat. To prevent this from happening, it’s essential to focus on strength and resistance training.
Strength training helps preserve lean body mass by signaling to your body that it needs to maintain muscle tissue. This is especially important when in a calorie deficit, as your body may turn to break down muscle for energy if it doesn’t receive the proper stimulus to maintain it.
Consistency and Hard Work: Key to Seeing Results
Consistency and hard work are key to seeing results from your workouts. It’s important to stick to a regular workout routine and gradually increase the difficulty over time.
Ensure you’re fueling your body with enough protein and carbohydrates to support muscle growth and recovery. Aim for at least 0.8 grams of protein per pound of body weight and consume complex carbohydrates like sweet potatoes, brown rice, and quinoa.
Finally, don’t forget about rest and recovery. Your muscles need time to repair themselves after strength training sessions, so ensure you get enough sleep and adequate rest days between workouts.
Importance of Nutrition and Exercise for All Body Types, Prioritizing Protein
Balanced Diet for All Body Types
Eating a balanced diet that includes all food groups is important for all body types, including skinny fat individuals. A balanced diet provides the nutrients to maintain good health and prevent chronic diseases. Many people often associate a balanced diet with weight loss, but it’s important to understand that a balanced diet is not just about losing weight. It’s about nourishing your body with the right foods in order to live a healthy life.
Protein for Muscle Mass and Fat Loss
Eating enough protein is crucial for maintaining muscle mass and promoting fat loss. Protein is an essential nutrient that helps repair and build tissues in the body, including muscles. For skinny fat individuals who have low muscle mass and high body fat percentage, consuming enough protein can help promote muscle growth while also aiding in fat loss.
Personalized Nutrition Plans
A nutritionist can provide personalized nutrition plans to help individuals achieve their health goals. They can assess an individual’s current eating habits, medical history, lifestyle factors, and personal preferences to create a customized plan that meets their specific needs. This option ensures that individuals are getting the proper nutrients they need without having to follow restrictive diets or fads.
Harmful Effects of Diet Culture
Diet culture often promotes restrictive eating habits, which can be harmful to both physical and mental health. Restrictive diets can lead to nutrient deficiencies, disordered eating patterns, and even eating disorders. Focusing solely on weight loss as a measure of success can lead to negative self-image and decreased self-esteem.
Understanding and Combating the Skinny Fat Body Type
In conclusion, skinny fat is a real health concern affecting many people. It is a body type where individuals have low muscle mass and high body fat percentage, which can lead to serious health risks such as diabetes, heart disease, and stroke.
Identifying if you are skinny fat can be done by measuring your body fat percentage and assessing your muscle mass. Once you know your body composition, you can improve your health by adding healthy habits such as strength training exercises and cardio workouts to help combat skinny fatness.
It’s important to prioritize protein while focusing on nutrient-dense foods like fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and healthy fats. By making these changes to your lifestyle, you can improve your overall health and reduce the risk of developing chronic diseases associated with being skinny fat or metabolically obese normal weight (MONW).
Remember that it’s about losing weight and building muscle mass. Strength training exercises like squats, deadlifts, lunges, push-ups, and pull-ups are great for building muscle, while cardio workouts like running or cycling can help burn excess body fat.
Incorporating these lifestyle changes may seem daunting at first but taking small steps towards a healthier lifestyle will make a big difference in the long run. Remember that being healthy is not just about looking good but feeling good too.
So if you fall under the skinny fat type or know someone who does – don’t ignore it! Please take action today by incorporating healthy habits into your daily routine and seeing the positive changes it brings.
.