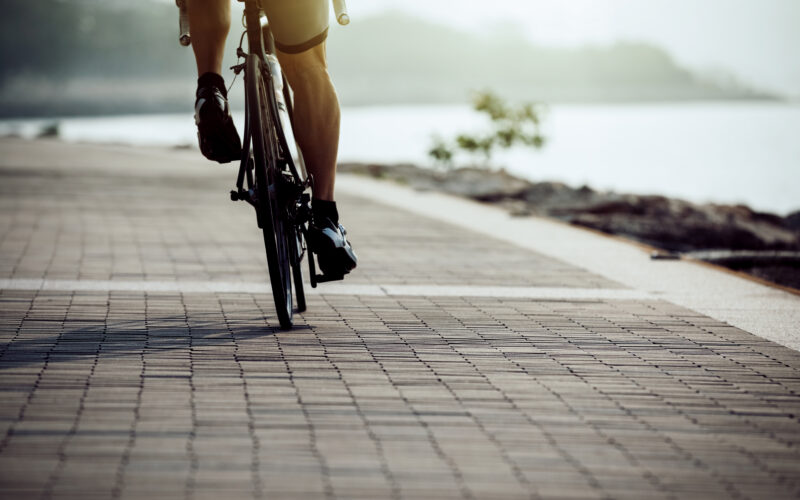
The Importance of Training Key Muscles for Cycling Performance
Training key leg muscles plays an essential role in improving cycling performance. Focusing on specific leg muscles can enhance power output and endurance during cycling. A review of studies shows that training the quadriceps, hamstrings, and glutes can significantly improve performance. Neglecting key leg muscles can decrease performance and increase the risk of injury for cyclists.
The quadriceps muscles are the large muscle group located at the front of the thigh. They are responsible for extending the knee and play a crucial role in generating power during cycling. Training the quadriceps through resistance training exercises like squats, lunges, and leg presses can improve power output and overall cycling performance.
 The hamstrings are located at the back of the thigh and work with the quadriceps to extend and flex the knee joint. During cycling, they play a critical role in generating power during each pedal stroke. Strengthening these muscles through deadlifts, hamstring curls, and glute-ham raises can improve endurance and reduce fatigue during long rides.
The hamstrings are located at the back of the thigh and work with the quadriceps to extend and flex the knee joint. During cycling, they play a critical role in generating power during each pedal stroke. Strengthening these muscles through deadlifts, hamstring curls, and glute-ham raises can improve endurance and reduce fatigue during long rides.
The Gluteus Maximus (glutes) are also essential for generating power during cycling. The largest muscle group in the human body is responsible for hip extension and stabilization while riding. Strong glutes can help prevent lower back pain, increase pedaling efficiency, and improve overall performance on hills or sprints.
Incorporating exercises that target these key leg muscles into your training program is crucial for improving your performance. However, it’s essential to remember that neglecting other muscle groups, such as calves or core, can also impact your overall performance on the bike.
With consistent effort focused on strengthening key leg muscles and proper nutrition habits, you’ll see significant improvements in your performance over time.
Primary Muscles Used in Cycling: Identifying the Key Muscle Groups
Quadriceps: The Powerhouse Muscle Group
The quadriceps are undoubtedly one of the most important muscle groups. These muscles at the front of your thigh are responsible for extending your knee and generating power during each pedal stroke. Without strong quads, maintaining a consistent pace or tackling steep inclines would be nearly impossible.
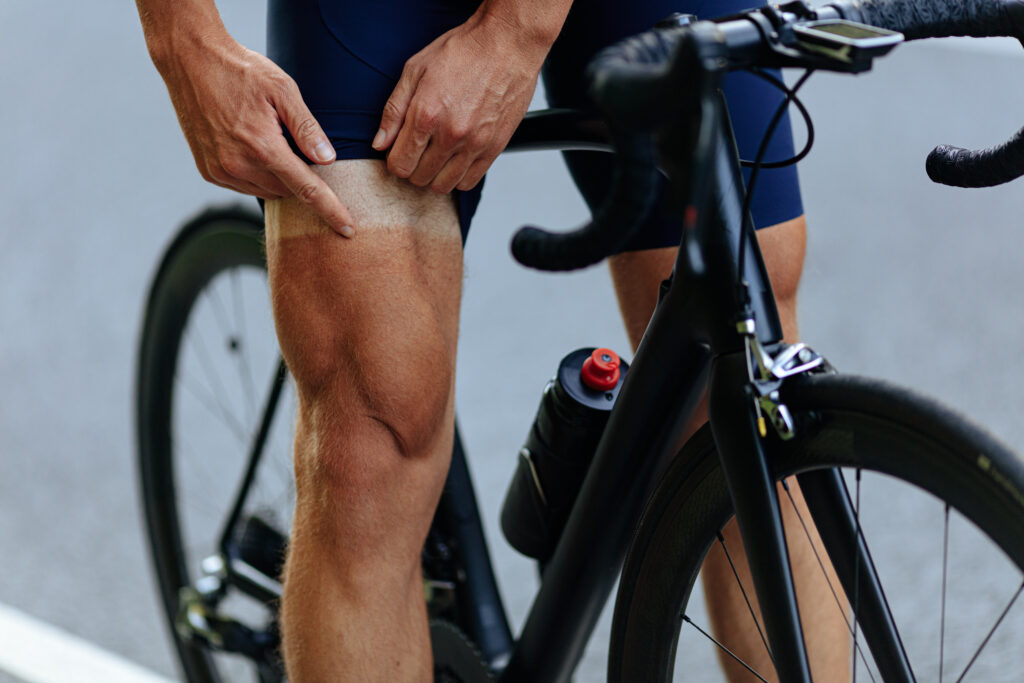 But why are the quadriceps so crucial in cycling? The answer lies in their ability to produce power through a wide range of motion. As you pedal, your quads contract and extend repeatedly, propelling you forward with each stroke. These muscles require significant strength and endurance, as they must work continuously throughout your ride.
But why are the quadriceps so crucial in cycling? The answer lies in their ability to produce power through a wide range of motion. As you pedal, your quads contract and extend repeatedly, propelling you forward with each stroke. These muscles require significant strength and endurance, as they must work continuously throughout your ride.
In addition to generating power, strong quads also provide stability and control during pedaling. They help align your knees and prevent wobbling or swaying on the bike. This is especially important when riding at high speeds or navigating tricky terrain.
Glutes and Hamstrings: The Primary Power Source
While the quadriceps play a significant role in cycling performance, they aren’t the only muscles at work. In fact, some experts argue that the primary power source during cycling comes from the glutes (butt muscles) and hamstrings (muscles at the back of your thigh).
The glutes are responsible for hip extension – essentially pushing your hips forward with each pedal stroke. This movement generates significant power and helps propel you forward on the bike. Meanwhile, the hamstrings work with the glutes and quads to complete this motion smoothly.
These three muscle groups form a powerful trio that drives performance. By strengthening all three areas through targeted exercises such as lunges, squats, and deadlifts – cyclists can improve their overall speed, endurance, and control on the bike.
Scientific Evidence Supporting the Importance of Cycling Muscles
Muscles Cycling Works: Scientific Evidence Supporting Their Importance
The glutes, hamstrings, and calf muscles are some of the primary muscles that cycling activates. However, there is more to the story than just these three muscle groups. Research has shown that cycling engages various muscles in the body, making it an excellent form of exercise for overall health and fitness.
Muscle Activation During Cycling
Cycling is a low-impact activity that can have significant health benefits. One of the reasons for this is that it activates multiple muscle groups at once. When you pedal a bike, your glutes, hamstrings, and calves, all work together to move your legs up and down. Your core muscles engage to keep your upper body stable while you ride.
In 2022, a study published in Sensors, compare muscle activation in the upper body and torso of people standing versus cycling. The study found that specific muscles, including the infraspinatus (part of the rotator cuff muscle group), latissimus dorsi (largest muscles in your back), external oblique (part of your core abdominal muscles), and pectoralis major (part of your chest), were more active during cycling. However, the level of activation was still relatively low. These muscles are important for cyclists, but other leg muscles may be even more crucial for cycling economy.
The activation of these muscles during cycling can lead to numerous health benefits. For example, regular cycling can improve cardiovascular function by increasing blood flow. It can also reduce stress levels by releasing endorphins in the brain.
The Role of Vastus Medialis Muscle
While many different muscles are involved in cycling, one muscle group is particularly important: the vastus medialis muscle (VMO). The vastus medialis is a muscle that is part of the quadriceps group. It starts from the top part of the femoral shaft and attaches to the quadriceps femoris tendon, which then connects to the upper part of the patella. The VMO is responsible for helping extend your leg when you pedal, which is a really important movement when cycling.
Lucky for us, an exercise called the terminal knee extension can help strengthen it! You can do this exercise at the gym using a resistance band or cable machine.
According to research published in the European Journal of Applied Physiology, twitch fibers are essential for generating power during high-intensity exercise like cycling. The VMO contains more slow twitch fibers than any other muscle in the quadriceps group and is critical for generating power during each down stroke.
Stretching After Cycling
After a long ride on your bike, stretching may be just what you need to prevent soreness and provide injury prevention. Stretching helps lengthen tight muscles that may have become shortened during exercise and improves flexibility.
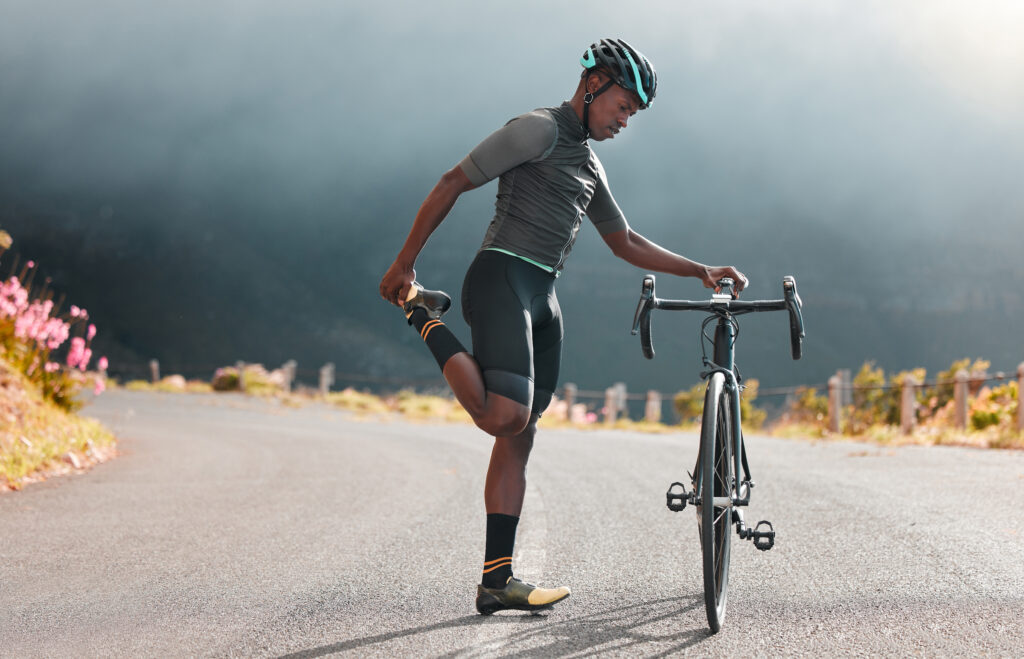 Stretching all major muscle groups after cycling – not just those used most during riding – is important as imbalances between different body parts can lead to pain or injury. For example, tight hip flexors can cause lower back pain, so stretching your hip flexors after cycling is crucial.
Stretching all major muscle groups after cycling – not just those used most during riding – is important as imbalances between different body parts can lead to pain or injury. For example, tight hip flexors can cause lower back pain, so stretching your hip flexors after cycling is crucial.
Muscle Imbalances
If your muscles are imbalanced, it can negatively impact your performance and increase the risk of injury. For example, if your quadriceps are significantly stronger than your hamstrings, you may experience knee pain while cycling due to an uneven distribution of force.
To prevent muscle imbalances, it’s important to engage in a variety of exercises that target all major muscle groups. Strength training exercises like squats and lunges can help build strength in the glutes and quads while also engaging the hamstrings and calves.
Training Strategies for Optimal Performance: How to Train Your Cycling Muscles
Incorporate Strength Training into Your Workout Routine
To improve your performance, it is crucial to incorporate strength training into your workout routine. Concurrent training will help you build muscle and increase your power output on the bike. The quadriceps, hamstrings, and glutes are the most important for generating power and endurance. Therefore, focusing on exercises that target these areas for optimal cycling muscle development is essential.
Focus on Exercises that Target Quadriceps, Hamstrings, and Glutes
Exercises such as squats, lunges, deadlifts, leg press, and step-ups are great for targeting the quads and glutes. These exercises help build strength in these muscles, translating into more power when pedaling up hills or accelerating from a stop. For hamstring development, exercises like hamstring curls or stiff-legged deadlifts can be added to your workout routine.
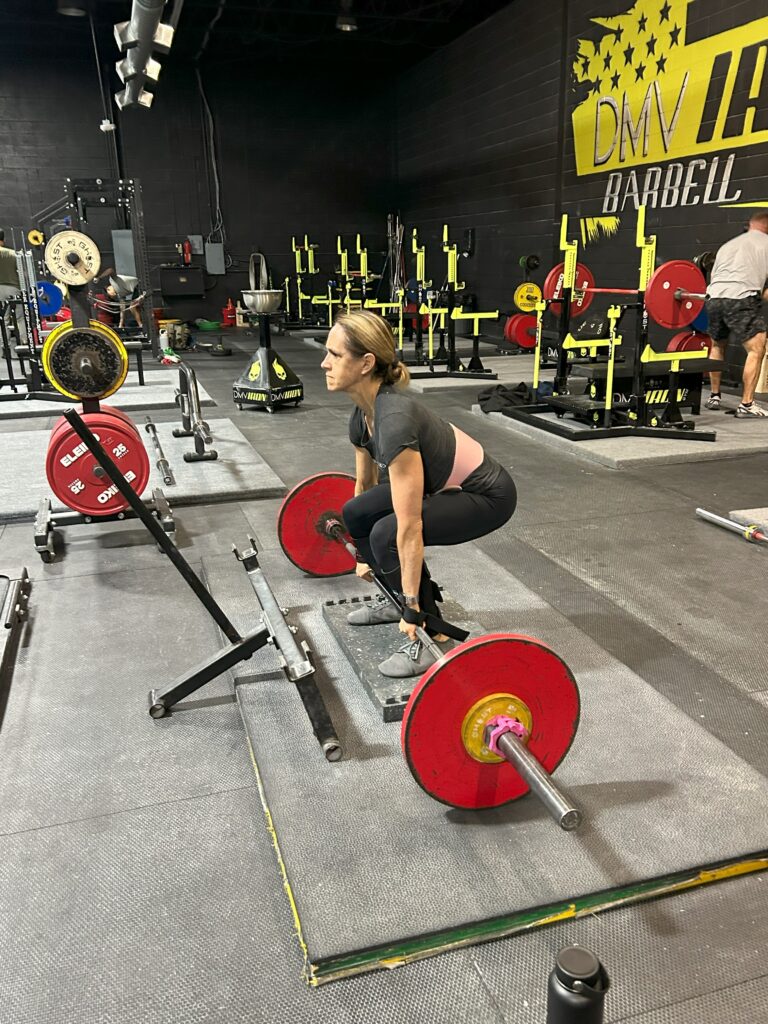

Implement Interval Training
Interval training is another effective way to increase endurance and build leg muscle stamina. Alternating between high-intensity efforts and periods of rest or low-intensity recovery work during rides or workouts can help you push through fatigue and build up your conditioning over time.
Training Your Core Muscles
While developing strong legs is critical for cycling performance, don’t forget about core stability training! A strong core helps maintain proper posture while riding, reducing fatigue in other parts of your body, such as arms or shoulders. Planks, sit-ups crunches are excellent core exercises for cyclists.
Riding Style Changes Which Muscles Cycling Works
It’s important to note that different riding styles may place varying demands on specific leg muscle groups. For example, road cyclists who spend long hours in the saddle at a steady pace may require more endurance-based training than mountain bikers who need explosive bursts of power for short climbs or technical sections.
Strengthening Your Legs with Cycling: Building Strength and Endurance
Cycling is a fantastic exercise for building leg strength and endurance. Whether you prefer indoor cycling or hitting the road, regular cycling can help you build muscular endurance in your legs while improving knee extension and calf muscles. Here are some important tips to keep in mind when it comes to strengthening your legs with cycling.
Regular Cycling Builds Muscular Endurance
One of the best things about cycling is that it helps build muscular endurance in your legs. When you cycle regularly, your leg muscles get stronger, allowing you to pedal for longer periods without feeling fatigued. This is especially beneficial for cyclists who want to improve their overall fitness and endurance levels.
Indoor Cycling Helps Increase Intensity
If you want to increase your workout intensity, indoor cycling is an excellent option. Indoor bikes allow you to adjust resistance levels and track your progress, making it easier to challenge yourself and push harder during each session. By gradually increasing the resistance on the pedals, you can build up strength in your legs over time.
Stretching Before and After Cycling Prevents Injury
Stretching before and after each cycling session can help prevent injury while improving flexibility. Stretching helps warm up your muscles before a workout, reducing the risk of strains or other injuries. After a workout, stretching helps cool down your muscles while promoting recovery.
Proper Pedal Stroke Builds Strength and Endurance
Focusing on proper pedal stroke technique can help you build strength and endurance in your legs more efficiently. To do this, focus on maintaining a smooth pedal revolution throughout each cycle rather than just pushing down hard with each stroke. By pedaling smoothly with proper form, you’ll engage all of the major muscle groups in your legs while minimizing stress on any one area.
Improving Upper Body Strength for Cycling: Training Your Arms, Shoulders, and Back
Upper body strength is an essential component of cycling that often gets overlooked. While the legs are undoubtedly the most important muscle group for generating power on the bike, a solid upper body can help maintain balance and stability, improve pedal stroke efficiency, and reduce strain on the hips and lower back. In this section, we will discuss why upper body strength is crucial for cyclists and how to train your arms (biceps femoris), shoulders, and back to improve your performance on the bike.
Maintaining a stable and balanced position on the bike is critical for any cyclist. A strong upper body can help achieve this by supporting your core muscles while you use your legs to generate force. Strength training exercises such as push-ups, pull-ups, rows, and overhead presses can target specific upper body muscles like arms, shoulders, and back. By increasing the strength of these muscles through regular training sessions, you can increase the force efforts of your entire body during cycling.
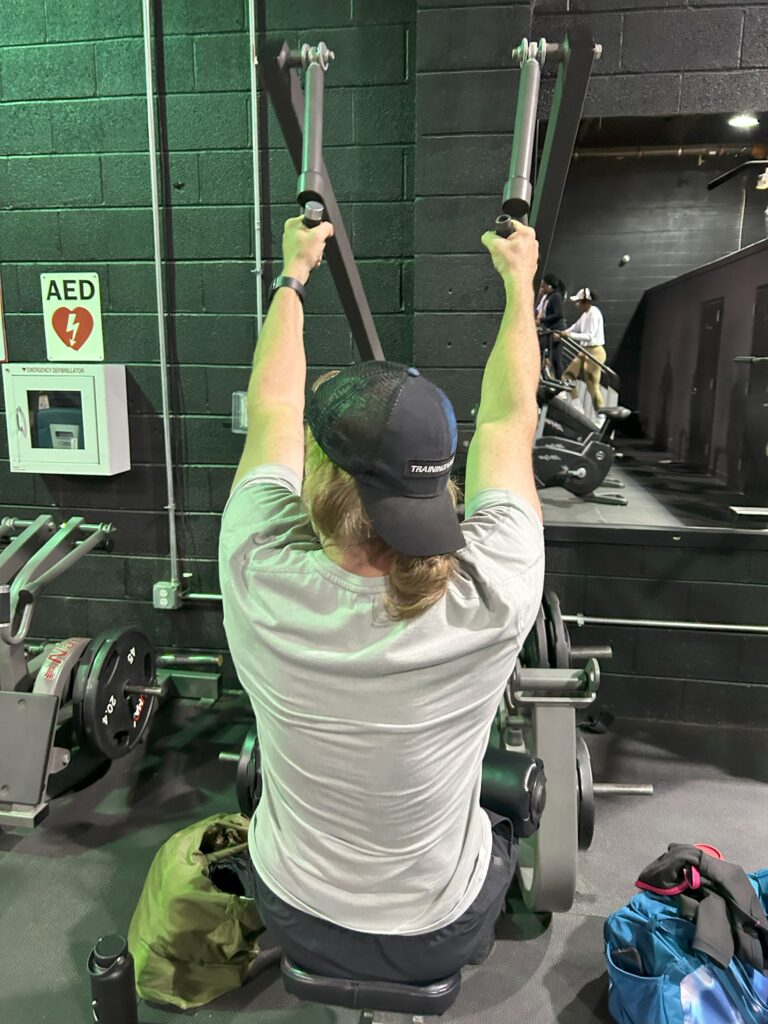 Core strength is also crucial for maintaining balance and stability while using upper body muscles to generate force. When you ride a bike at high speeds or tackle challenging terrain like steep hills or sharp turns, it’s essential to have a strong core to keep you upright and in control. Exercises like planks, sit-ups, Russian twists, and bicycle crunches can strengthen your core muscles while improving your overall bike posture.
Core strength is also crucial for maintaining balance and stability while using upper body muscles to generate force. When you ride a bike at high speeds or tackle challenging terrain like steep hills or sharp turns, it’s essential to have a strong core to keep you upright and in control. Exercises like planks, sit-ups, Russian twists, and bicycle crunches can strengthen your core muscles while improving your overall bike posture.
Maintaining a strong, stable upper body position can also improve pedal stroke efficiency. When you’re pedaling with maximum power output from your legs but lack stability in your upper body position due to weak arm or shoulder muscles – it becomes difficult to transfer that power efficiently onto the pedals without wasting energy or losing momentum. By strengthening these muscle groups through targeted exercises like bicep curls or tricep extensions – you’ll be able to maintain optimal form throughout each pedal stroke cycle.